THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEM
Save your excess and use it on demand
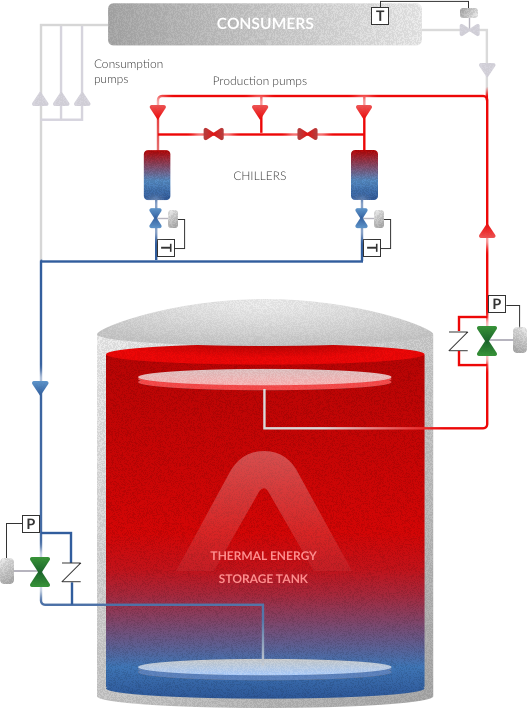
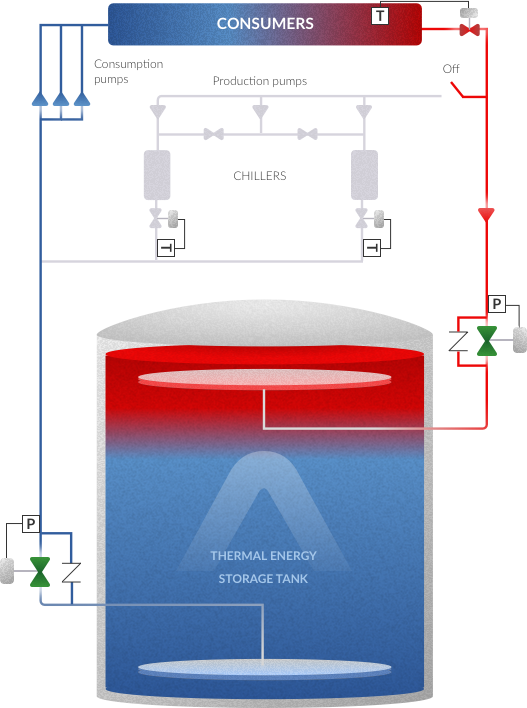
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) systems are accumulators that store available thermal energy to be used in a later stage when consumption is required or when energy generation is cheaper. A TES tank reduces the operational cost and the required capacity of the Cooling and Heating plants, increasing the efficiency and reducing the capital cost.
This is our most popular type of Thermal Energy Storage System. In a naturally stratified chilled-water storage tank, cold and warm volumes of water are stored together without a physical barrier. A stable density gradient prevents the mixing of the two volumes. The proper design of diffusers is able to maintain the stable and reduced gradient during the complete operation of the tank.
Typically, there will be a 0.4 to 0.6m thick thermocline (a region with vertical temperature and density gradients) making a separation between the cold and the hot water. In discharging mode, cold water is withdrawn from the bottom diffuser and warm water returns to the top of the tank. Regarding the charging mode, cold water is introduced from the bottom diffuser and warm water is withdrawn from the top of the tank.
Ice TES Tank uses the latent heat of fusion of water to store cooling. Thermal energy is stored in ice at the freezing point of water (0 ºC), via a heat transfer fluid at temperatures that range from -9 to -3 ºC.
Depending on the ice thermal storage technology selected, the chillers shall be selected accordingly. The heat transfer fluid for ice-making may be a refrigerant or a secondary anti-freeze coolant, such as glycol. The low storage temperature of ice also provides the ability to produce lower temperature air for cooling.
The main Ice Storage technologies: Ice harvester, internal melt-on-coil, and external melt-on-coil and encapsulated ice.


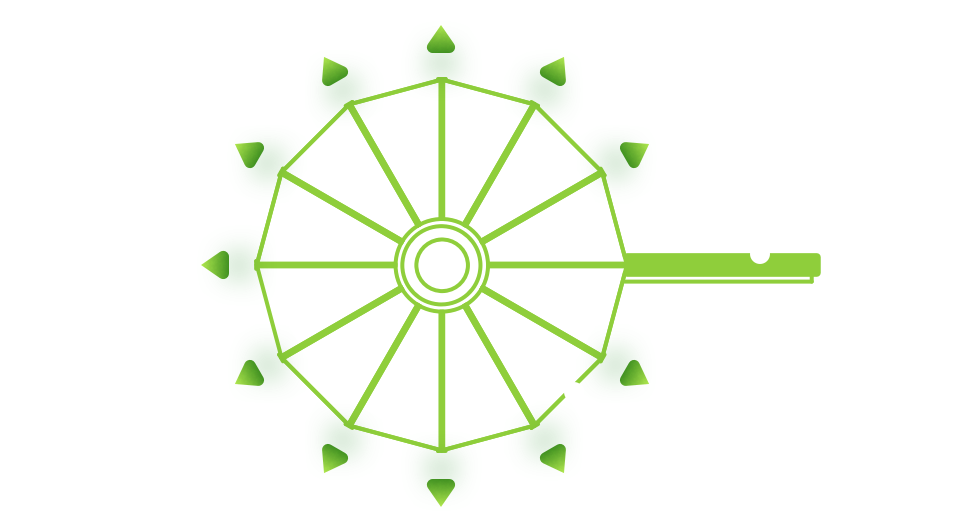
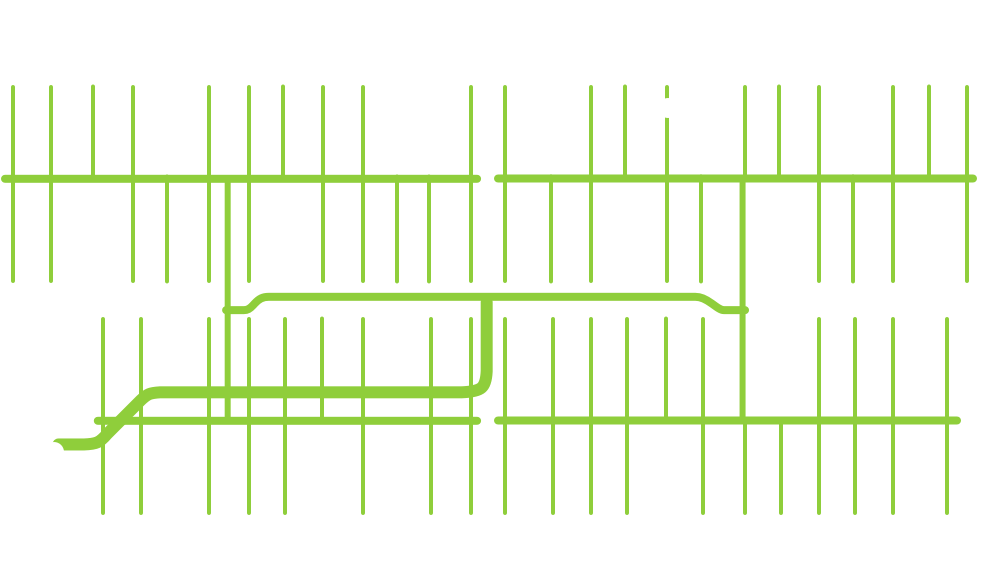
Diffusers are used in our Stratified Water Tanks to maximize the efficiency of the TES system by minimizing the thermal losses. The ARANER designed diffuser systems help to preserve stratification by minimizing the disturbance caused by inlet and outlet flows, supported by extensive CFD studies and R&D of new diffusers.
REDUCES CAPITAL COSTS due to sizing for average demand.
REDUCES the required capacity of the cooling plant.
REDUCTION in greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants.
LESS WASTED energy and resources.
USE OF EXCESS COOLING CAPACITY production to meet peak cooling demands.
REAL-TIME MONITORING of the temperature at different levels of the tank.
INCREASES ELECTRICAL EFFICIENCY by reducing power consumption, coordinating with peak power demands.
They were looking for a thermal storage tank to store the chilled water into it and supply when the actual load is less than what is produced by the chillers.
Reduce the operational cost and the required capacity of cooling & heating plants. Get better performance and increase the reliability of the system.
We invite you to download it for FREE and discover all the advanced features.
Solve any doubts through our frequently asked questions or ask for advice
FAQ's about TESWe create solutions and guarantee success by taking full responsibility of the overall project.