The world is facing two headaches in regards to energy development: new sources of energy and innovation of affordable and efficient energy storage systems. Energy wastage is a chief concern and the solutions provided by stratified thermal energy storage systems give a massive boost to cost saving measures. For those wondering what stratified TES actually is and how it can help to reduce the capital cost and increase the efficiency of the cooling plant, let us review this system, focusing on the thermal energy storage tanks. Stratified TES system has been in existence for more than three decades. This is not to say this is the only system in the thermal energy storage cadre. In the 70s and 80s, many of them were in the trial phase, but the stratified thermal came out tops because of its low cost and simplicity. The first commercial application of this technology was in the 80s, in areas such as industries, passive solar, passivhaus buildings, incineration or power plants.
| TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| Thermal Energy Storage Tank: the Main Component |
| Charging Operation |
| Discharging |
| Important Benefits of Stratified TES Tanks |
| Future and Challenges of Stratified Energy Storage Tanks |
Thermal Energy Storage Tank: the Main Component
The thermal energy storage cylinder or tank is the most important part of the stratified TES system. Although this solution is mainly associated to a cylindrical form, which suits some industries, this design is not exclusive. For instance, ARANER’s thermal energy storage tanks or tanks are tailor-made, and can be designed and manufactured in whichever shape bests suits the particular industrial necessity or the power augmentation plant it will be included in. 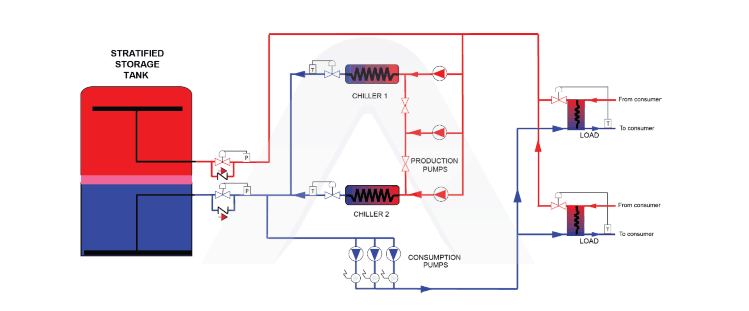
The principle of stratified TES tank operation is based on thermal stratification process. Stratification is just a natural process: the warmth and density of water are inversely proportional properties. This means that warm water will always settle on top of cold water. We can analyze the process that takes place in a stratified thermal energy storage tanks in terms of two operations: charging and discharging. [hs_form id="13"]
Charging Operation
This operation starts when the tank is full of warm water. Slowly and regularly, the water is replaced by chilled water. The chilled water is supplied from a separate chiller unit. This replacement occurs for several hours, leading to a point where there is no longer warm water in the tank and only the colder water is left.
Discharging
This is the opposite of the charging process. For several hours, cold water is removed from the tank through diffusers located at the bottom. Warm water enters the tank through diffusers placed at the top of the tank to replace the cold water . The Figure below shows one type of a diffuser(s). Diffusers are critical in both processes because they minimize the mixing of different layers of water.
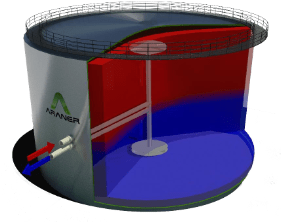
The thermal energy storage tank is always full, but the interface between cold and warm water (thermocline) moves up and down depending on whether the system is charging or discharging. The thermocline can be as thick as 1m during charging and discharging. Stratified TES Tanks’ design encourages their correct operation. Their extensive height allows the water to form heat layers (stratification), which is a natural phenomenon. Other than height, designers at ARANER consider tank diameter, figure of merit, outlet temperature and inlet temperature.
Important Benefits of Stratified TES Tanks
Thermal Energy Storage solutions are well considered by energy specialists for economic reasons. For companies with energy peaks, this solution will be more economical than the installation of an entire new energy production system. However, this is only one of its benefits.
- Energy Efficiency: ARANER tanks are able to minimize energy loss and save the peak energy capacity. We use state-of-the-art measurement technologies which ensure that the charging and discharging cycles are reliable.
- Optimum Process: Every project has a unique load curve that determines the charge and discharge rates, as well as the energy capacity of the system. To serve a wide range of applications, ARANER tanks are available in different shapes and sizes: our solutions are tailor-made for customer unique requirements to perfectly suit TIAC and District Energy solutions.
- Reliable Material: The tanks are made with corrosion resistant material. More importantly, the material is capable of maintaining stratification for long periods. Simply said, its thermal insulation properties are excellent.
When it comes to materials, stratified TES tanks can be made from different materials that include steel, concrete and plastic. For steel tanks, the main challenge is rusting. With epoxy coating, this problem is manageable. Concrete tanks can be integrated with the building, thereby bringing savings. Plastic tanks are rarely used, but are still applicable. UV stabilizers may be required because sunlight can be detrimental to this material.
Future and Challenges of Stratified Energy Storage Tanks
Though stratified TES is inexpensive, there are still problems in regards to low energy density and complexity in designing the storage tanks. The good news is that the technology is still undergoing developments to improve materials and techniques. At ARANER, we are constantly innovating and looking for the solutions that will help you achieve the expected results in power augmentation and energy efficiency. Our Thermal Energy Storage technology, in combinations with TIAC solutions, allows for a reduction in operation costs and refrigerant plant capacity requirements. Learn more about our comprehensive TES solutions or contact one of our experts for more information.










