The process for industrial decarbonisation remains a crucial part of the effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the context of harm reduction measures for climate change.
While the industrial sector is accountable for an important part of these harmful emissions, it’s also true that this economic sector has also taken significant measures to reduce this impact. From improving efficiency ratios and minimizing energy consumption, many progresses have been made towards industrial decarbonisation.
This has also been accompanied by governmental actions across different territories, as public institutions are willing to provide funding for switching to alternatives. This includes the incorporation of efficient technologies such as industrial heat pumps, as we’ll see below in this article.
What is industrial decarbonisation and why is it important
The term industrial decarbonisation refers to the multiple efforts undertaken to replace fossil fuels with low-carbon sources that minimize the environmental impact of industrial activities.
While a majority of energy generation processes today come from fossil fuels, major attempts are being made to try to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In such a context, several actions stand out, including the switch towards more efficient technologies such as industrial heat pumps (IHPs) for their capacity to significantly reduce energy and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
The need for industrial decarbonisation is essential considering this sector’s big impact on harmful emissions. In fact, globally, energy production accounts for 73.2% of emissions. Within this percentage, the energy use by the industry accounts for 24.2%, according to figures by Our World in Data. This same source confirms carbon emissions directly related to industrial processes account for 5.2%.
The challenges surrounding industrial decarbonisation
- The main challenge of industrial decarbonisation is related to the fact that the industrial sector remains one where energy consumption is intense.
- Different industrial sectors present varying degrees of energy and raw material needs. This means measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions cannot be applied following a single standard, but must adapt to the specific needs of each sector.
- Measures surrounding industrial decarbonisation should also take into account the need to avoid major disruptions in industrial competitiveness particularly for strategic players.
Fortunately, the technologies enabling industrial decarbonisation are also evolving to provide solutions to these challenges. These include the move towards alternative sources of energy and the use of efficient equipment, such as industrial heat pumps.
The key measures for industrial decarbonisation today
Focusing on energy efficiency
The concept of energy efficiency refers to the capacity of certain processes to generate energy while minimizing the amount of resources used, including the employment of fossil fuels and the ensuing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
The incorporation of industrial heat pumps represents one such move. Research shows that industrial heat pumps can cut energy used by one-third, generating a significant impact in the effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing carbon intensity
Industrial decarbonisation processes also focus on eliminating CO2 emissions across the whole production chain, from the extraction of raw materials to their transformation into products and their distribution and use.
The move towards alternative energy sources with zero or minimum emissions is included in this category.

Strategies to capture CO2
A number of technologies now allow to capture, store and then use CO2 emissions generated in industrial processes.
Developing circular economy models
Circular economy refers to the production models where product life cycles are extended by guaranteeing they can be reused or recycled, in an effort to minimize waste. While this can apply to material products, the circular paradigm can also concern energy waste. The use of cutting-edge technologies, such as TES tanks for thermal energy storage, applied to energy generation via heat pumps represents a key example of this.
Industrial heat pump benefits for decarbonisation
Industrial or large-scale heat pumps are technologies used to produce heating energy. In order to do so, they follow the heat pump cycle principle, which consists of transferring heat from a cold system to a hot one, following the Reversed Carnot Cycle.
While this technology has been around for many decades, the need for industrial decarbonisation has put industrial heat pumps on the spot today. This is because they provide solutions to many of the main challenges cited above in the quest for a carbon-neutral future:
-
They’re extremely energy efficient. Heat pump technologies have been shown to generate a 20% increase in heat recoveries and unmatched COP efficiencies of between 3 to 6 units.
-
They provide immediate relief from greenhouse gas emissions. Moderate estimates show that deployment of IHPs could avoid emissions of 12–25 million metric tons/year of CO2. This is key considering how legislations are increasingly focusing on restricting the different industries’ carbon footprint: bans, taxes and other reforms are pushing industrial companies to shift their processes towards a net-zero carbon footprint. In this context, the shift towards heat pumps represents a key choice to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve the ecological transition
-
They reduce operating costs, thus providing a viable solution for industrial decarbonisation.In fact, high-performance heat pumps present lower annual costs than other alternatives, providing an effective counterbalance and return on investments: paybacks on investment can be be less than 2 years
-
They offer the possibility to incorporate sustainable, local and non-fuel heat sources
-
They are a viable model for developing circular economy models. Industrial heat pumps are able to use available local energy sources, as well as making the most of waste energy and recovering it.
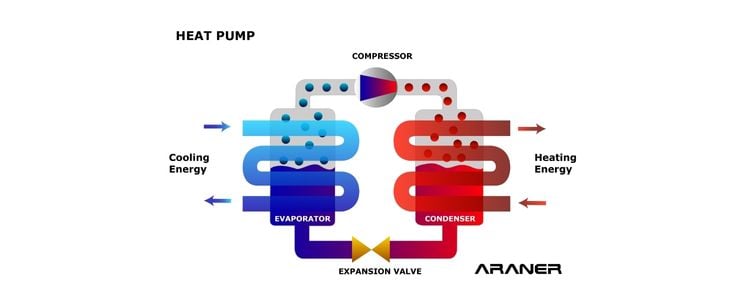
The benefits associated with industrial heat pumps have put this technology at the center of many crucial transformations in the way heat is obtained. As such, they already play a key role in the switch towards sustainable district heating, including innovative solutions such as the use of seawater heat pumps and geothermal heating.
At ARANER, we work to become trustworthy and reliable partners in the shift towards sustainable and efficient energy technologies in the wider context of industrial decarbonisation.
As such, we offer a wide variety of industrial heat pumps, as well as our decades-long expertise in order to develop end-to-end solutions, from design to implementation and maintenance.
Want to learn more about industrial decarbonisation and how industrial heat pumps are helping major industry players to make the move towards efficiency and sustainability? Download our free ebook about district heating technologies and heat pumps or get in touch with us and speak to our team about the opportunities that best adapt to your project.









