R717 Advantages
- Natural refrigerant, environmentally friendly. Doesn't contribute to global warming
- Self-alarming pungent odor
- Highly energy efficient vapor compression cycle, thus less energy consumption
- Longer life expectancy, thus reduced operational costs during full life cycle
- It can be used in conjunction with other secondary fluids such as water or glycol, for absorption cooling applications
R717 Drawbacks
- Flammable at high gas concentrations when mixed with air
- Installation cost
- Specific training for technicians handling ammonia
In every cooling plant using chemical refrigerants, it is compulsory to perform a risk assessment for a proper operation and maintenance of the plant and to provide correct safety measures for emergency events. In case of ammonia, one of the safety aspects to be considered is the event of high gas concentrations after a leak, which can lead to explosion if the same is not properly handled.

Ashrae 15 and IIAR 2
For this purpose, there are standards such as Ashrae 15 or IIAR-2 defining the safety principles for the plants using ammonia as refrigerant. These standards set different limits based on ppm concentration and regulate the behavior of the ventilation and emergency system requirements of the plant. Depending on gas concentration, exposure to ammonia can cause several breathing problems, eye irritation and skin burns. The toxic effects and human exposure limits to ammonia are listed below:
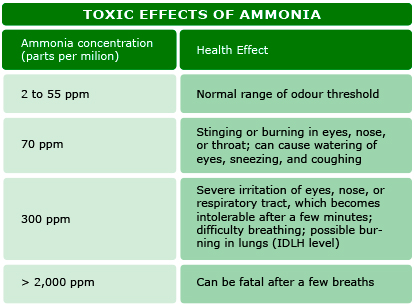
Table 1a: Toxic effects of R71
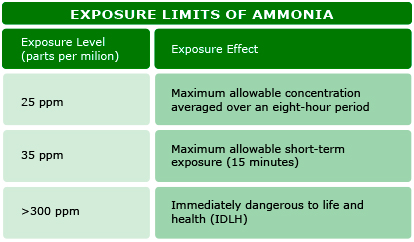
Table 1b: Exposure limits to R717
Detection and Alarm
Based on levels shown in table 1a and 1b, the standard IIAR 2 defines certain detection and alarm levels to be implemented in different areas of ammonia plants, it defines also the alarm response for each ppm range of refrigerant. The main ammonia detection and alarm levels included in IIAR 2 are mentioned below: Level 1 shall have the following features:
- At least 1 ammonia detector shall be provided in the room or area
- The detector shall activate an alarm that reports to a monitored location so that corrective action can be taken at a level no higher than 25 ppm.
- At least 1 ammonia detector shall be provided in the room or area
- The detector shall activate an alarm that reports to a monitored location so that corrective action can be taken at a level no higher than 25 ppm.
- Audible and visual alarms shall be provided inside the room to warn that, when the alarm has been activated, access to the room is restricted only to authorized personnel and emergency responders.

Figure 1: Visual and audible alarm equipment
Level 3 shall have the following features:
- At least 1 ammonia detector shall be provided in the room or area
- The detector shall activate an alarm that reports to a monitored location so that corrective action can be taken at a level no higher than 25 ppm.
- Audible and visual alarms shall be provided inside the room to warn that, when the alarm has been activated, access to the room is restricted only to authorized personnel and emergency responders. For machinery rooms, additional audible and visual alarms shall be located outside of each entrance to the machinery room.
- Upon activation of the alarm, control valves feeding liquid and hot gas to equipment in affected area shall be closed, and pumps, fans or other motors associated with the ammonia refrigeration equipment in the room shall be de-energized.
- Upon activation of the alarm, emergency exhaust systems, where required, shall be activated.
Alarm Response
The IIAR 2 standard defines safety actions associated with each alarm level. For this purpose, every ammonia plant needs to comply with the following requirements related to electrical system: Ammonia concentrations levels of less than 25 ppm requires no alarm response. In case of concentrations equal or exceeding 25 ppm, visual indicators and audible alarms shall activate. The fans (not strictly dedicated for ammonia exhaust) shall be stopped and dampers closed in order to avoid accidental spread of ammonia vapor. If ammonia concentration drops below 25 ppm, the visual and audible alarm shall be permitted to be automatically reset For concentrations above 160 ppm, visual and audible alarms shall be activated and also the emergency ventilation. Once activated, emergency ventilation will continue operating until manual reset by a switch located in machinery room. In case of detection of ammonia concentrations that exceed detector upper limit or 40,000 ppm (whichever lower), visual alarm, audible alarm and emergency ventilation shall be activated, and will continue operating until manually reset. In addition to this, the following equipment in the machinery room shall be automatically de-energized:
- Refrigerant compressors
- Refrigerant pumps
- Normally closed automatic refrigerant valves.
Electrical Safety Requirements
Area Classification: The room containing equipment with ammonia refrigerant is classified as ordinary location where the room is provided with emergency ventilation. The rooms without emergency ventilation will be classified not less than Class I, Division 2, Group D Hazardous (Classified) Locations, and electrical equipment installed in the machinery room shall be designed to meet this requirement. Emergency stop switch: There must be a clearly identified emergency shut-off emergency switch equipped with temper resistant cover installed outside and adjacent to designated principal machinery room door leading outdoors. This switch shall provide “off-only” control of refrigerant compressors, refrigerant pumps and normally closed automatic refrigerant valves located in machinery room. The function of the switch shall be clearly marked by signage near the controls.
4"] 
Figure 2: Ammonia alarm switch and Compressor Emergency shut-off button
Emergency ventilation control switch: The room shall have a clearly identified control switch for emergency ventilation equipped with a temper resistant cover which shall be located outside and adjacent to the designated principal machinery room door leading to outdoors. This switch shall provide “ON/AUTO” override capability to start emergency ventilation. Additionally, the function of the switch shall be clearly marked by signage near the switch location.

Figure 3: ON/Auto switch and Emergency shut-off panel with ppm indication
Lighting requirement: The machine room with ammonia refrigerant operated equipment shall be equipped with light fixtures delivering a minimum of 320 lux at the working level, which is 0.91m above floor or a platform. Ventilation & Emergency ventilation: Multiple fans or multispeed fans are allowed for temperature control and emergency ventilation of the machinery room. Normal ventilation can be activated either from temperature control (thermostat) or by the emergency ventilation switch. Emergency ventilation shall be designed to provide not less than 30 air changes per hour based on machinery room volume. Emergency ventilation shall be activated by ammonia leak detector or by manual control.

Figure 4: Machine room exhaust fan status indication
Others: All machinery rooms with ammonia equipment shall be furnished with self-closing and tight-fitting doors. The access to refrigerating machinery room shall be restricted to authorized personnel, this can be done with multi-level access control system.
Conclusion
Ammonia or R717 is a refrigerant with excellent properties such as increased cooling capacity and efficiency compared to other refrigerants, but the plants using R717 need to be very strict in compliance with the safety guidelines provided in the standards, mainly IIAR 2 and ASHRAE. The standard has certain requirements which define the safety measures of the plant to minimize the human and material damages in the event of ammonia leak. Some of these requirements are related to electrical system, such as ventilation, lighting, shut-off switch, on-auto switch for ventilation, etc. As a conclusion, cooling plants using R717 will be of higher efficiency considering energy consumption, and for a certain cooling capacity will require less amounts of refrigerant. As long as all safety measures provided in the standards are complied, the plant operation and maintenance will be as safe as with other refrigerants. The electrical system shall adapt to such measures, i.e provide the necessary inputs in compressor motor feeders for emergency shutdown or external starting inputs in the exhaust ventilation feeders. Get in touch with ARANER about your chilling plant!









