Gas turbines are without doubt very popular in the arena of power plants. Here you will find two main types: industrial and aeroderivative gas turbines . You have to appreciate that many turbines in the market take a long time to start, mainly because the heat must have enough time to penetrate the thick metal sections.
High turbine inlet temperature is also a challenge
While start up time is not a problem for aeroderivative turbines, ambient conditions still reign supreme if a power plant fails to employ available solutions. This post is about power augmentation through temperature control, but first is a review of aeroderivative gas turbine technology and power losses associated with it .
History and applications of Aeroderivative Gas Turbines
Power generation and aeroderivative gas turbines are almost synonymous with each other. Aeroderivative gas turbines were the first in the turbine family to be used in power generation. When they emerged for stationary power, they were used for peaking power applications. Since the 1940s, the complex machines have portrayed high efficiency and reliability despite being lightweight. These impressive characteristics have seen the turbines increase in popularity and inspire new divergent uses. As mentioned earlier in this post, these gas turbines are vastly used in peaking power plants . They fit so well in these applications because of their fast start up and stop capabilities and excellent load following. It is for the same reasons that the devices are popular for grid stability for grid tied wind and solar energy systems. The other market for aeroderivative gas turbines is district heating and cogeneration . Applications in this category use both electricity and heat produced by the turbine. Finally, you will find the turbines in mobile power applications . The machines are suitable for such use because they are lightweight, fuel-flexible and easy to use. Like other industrial machines, these turbines are susceptible to losses, some of which can affect plant performance and profitability.
Sources of power loss
The aeroderivative gas turbine has to match the grid frequency and operate at a fixed speed. This means that fuel amount almost solely determines the amount of power the machine can generate . However, several other factors also affect the efficiency and power output of the device:
- Relative humidity
- Atmospheric pressure
- Air filters-pressure drop
- Compressor fouling
- Ambient temperature
Among these factors, ambient temperature is the most prevalent one . As inlet air temperature increases, the specific volume of air increases too. This has a direct effect on power output of the turbine because it reduces mass flow of air. If you have not taken care of this factor in your GT power plant, you might want to contact ARANER for a reduction in capital and operation cost . Of course, this is through the very reliable Turbine Inlet Air Cooling (TIAC) solution .
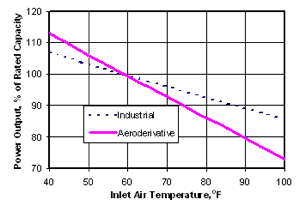 Fig 1: Graph showing relation between power output and inlet air temperature for turbines
Fig 1: Graph showing relation between power output and inlet air temperature for turbines
TIAC for reliability and flexibility
Which plant manager or proprietor does not want constant power output? With TIAC you can achieve higher and constant performance from your machine. The technology has been installed in hundreds of instances across the world and the feedback is excellent. One important thing to note about TIAC: it is independent from the wet bulb temperature . What does this mean? This implies that you can use the solution anywhere including coastal humid environments. This is a very suitable solution because gas turbines are generally very complex; any measure to increase performance is bound to have an economic impact. Temperatures of up to 1700 degrees centigrade require advanced blade design and extremely strong materials. That’s why reducing inlet air temperature through TIAC is the goal of most power plants today. Power plants in the Middle East and regions with similar conditions are turning to TIAC technologies for power augmentation purposes. Do you think ARANER’s solutions could be the answer you have been looking for?
To conclude
In this post we have described the characteristics and applications of aeroderivative gas turbines . We have also reviewed how the turbines lose power and how TIAC is a suitable remedy to this drawback. It should not be lost to you that there are several TIAC solutions. Ultimately, your choice determines the effectiveness of the solution in overcoming effects of ambient conditions. With ARANER’s experts , you can get your plant performance and weather data detailed as part of an extensive analysis. This will then enable your power plant to adopt a solution that makes it operate reliably, safely and without the need for increased chiller capacity.










