From manufacturing processes to district cooling efforts, choosing the right chiller is an important decision for many companies, impacting both energy efficiency and performance. In fact, choosing a chiller that matches the application’s cooling load is a crucial step for an efficient and reliable cooling performance.
Let’s then look at questions such as what air cooled chillers are and how they work, as well as the advantages of different chiller technologies.
What is an air cooled chiller
An air cooled chiller is a type of cooling system that uses ambient air as the heat rejection medium from a space.
It works by circulating water or other fluids through a system to absorb heat and lower the temperature of the area or equipment. In other words, the chiller is not in charge of generating cold: it dissipates heat, facilitating its transference outside of the allocated space.
There are various applications of air-cooled chillers: they’re used on industrial processes, data center cooling, HVAC and district cooling.
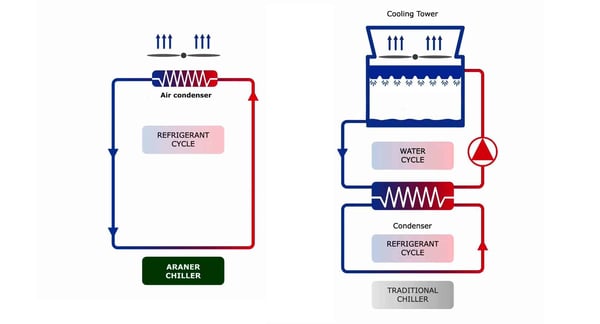
How air cooled chiller works: a comparison between the three types of chillers
1. Air-cooled scroll and air-cooled screw chillers
An air-cooled scroll chiller is a specific type of air-cooled chiller that utilizes scroll compressors as the primary cooling technology. On the other hand, air-cooled screw chillers employ screw compressors as the primary cooling technology.
Both use ambient air as the heat rejection medium to remove heat from a space. They follow a refrigeration cycle that starts with a compressor acting on the refrigerant gas and increasing its temperature. This marks a difference with absorption chillers.
Then comes a condenser, which is in charge of liquefaction. Passing through an expansion valve, pressure and temperature of the refrigerant are reduced, so that it evaporates. It’s now time for the heat absorption in an evaporator. After performing this task, it’s ready to repeat the cycle.
What these two air-cooled chillers have in common is their suitability for smaller process applications, with a simple installation and low water consumption. However, they present a limited cooling capacity and efficiency, so they’re only adequate for small residential projects or medium-sized towers.
2. Water-cooled chillers
A water-cooled chiller represents an alternative to air-cooled chillers. They employ specific cooling towers and can present high efficiencies as liquids offer better heat transfer capabilities.
The working principle of water-cooled chillers follows a logic in which evaporator, to compressor, condenser and expansion valves are employed. Again, through the interchange of the material’s temperatures and pressures, water can act as a cooling agent.
These solutions are suitable for higher cooling loads, such as district heating projects. In fact, they are employed in large and medium-sized structures and buildings. However, its high use of water resources must be considered, both for environmental as well as economic reasons. Their use involves using a large amount of water.
However, water-cooled chillers offer several additional advantages over air-cooled solutions. This includes taking up less space and a reduction in maintenance and repair costs.

3. Magnetic-bearing chiller turbocompressors
The comparison between air-cooled and water-cooled compressors should take into account this innovative approach. This type of chiller compressors represent a recent solution for high efficiencies compared to screw and scroll chillers.
The process begins with the compressor acting on the refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature. Then, the refrigerant passes through a condenser where it liquefies. After that, it goes through an expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature, causing it to evaporate and absorb heat in the evaporator.
As such, they’re increasingly incorporated into high-cooling load solutions, such as district cooling initiatives. In fact, the U.S. Department of Navy quantifies there are now 35,000 of these, logging over 55 million run-hours just in the U.S. These include their application in many diverse sectors, from the plastics industries to pharmaceutical and exceedingly efficient cooling initiatives. The key for their outstanding efficiencies lies on several distinctive factors.
On the one hand, it removes oil from the equation. The magnetic bearings allow the compressor to operate without oil for lubrication. This has an enormous impact on facilitating and reducing maintenance costs, but its impact goes beyond that. The lack of oil reduces energy losses and maximizes heat transfer efficiency, as oil doesn’t enter evaporators or condensers.
Additionally, this approach to zero-oil in cooling equipment improves the U-Value inside heat exchangers, as verified by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE).
All heat transfer rates and bubble size values experiment optimizations in this type of equipment, which then has an impact on costs and maintenance needs. The result is a 49% average power savings achieved, as identified by the U.S. Navy Techval and a 6.4 years average return on investment.
These chillers are ideal for district cooling initiatives and large structures due to their high cooling capacity and efficiency. They also operate quietly and efficiently at partial loads, making them suitable for various applications.Their light weight allows for a faster installation.
All in all, a magnetic-bearing chiller compressor can be a good option both for new and retrofit projects, as well as chillers that run at partial load a majority of the time. They deliver a better energy performance and great savings in energy costs, thus becoming a preferred option for a number of projects.
All things considered, cooling engineers and designers should take into account the options outlined above when making a choice. At ARANER, we work to provide projects with their most suitable cooling solutions. As such, we offer cutting-edge centrifugal and magnetic-bearing compressors to fit our state-of-the-art district cooling solutions.
Get in touch with us and find out more about how we can help you.










